Bootstrap Button Input
Introduction
The button components coupled with the urls covered inside them are probably some of the most significant features helping the users to interact with the website page and move and take various actions from one web page to another. Most especially these days in the mobile first industry when about half of the pages are being watched from small-sized touch screen machines the large comfortable rectangle places on display very simple to discover with your eyes and tap with your finger are even more necessary than ever. That's reasons why the brand new Bootstrap 4 framework progressed presenting extra comfortable experience dismissing the extra small button size and incorporating some more free space around the button's captions making them more legible and easy to use. A small touch bring in a lot to the friendlier appearances of the brand new Bootstrap Button Switch are at the same time just a little bit more rounded corners that along with the more free space around making the buttons much more satisfying for the eye.
The semantic classes of Bootstrap Button Toggle
Here in this version that have the very same number of simple and marvelous to use semantic styles giving us the capability to relay explanation to the buttons we use with simply just adding a particular class.
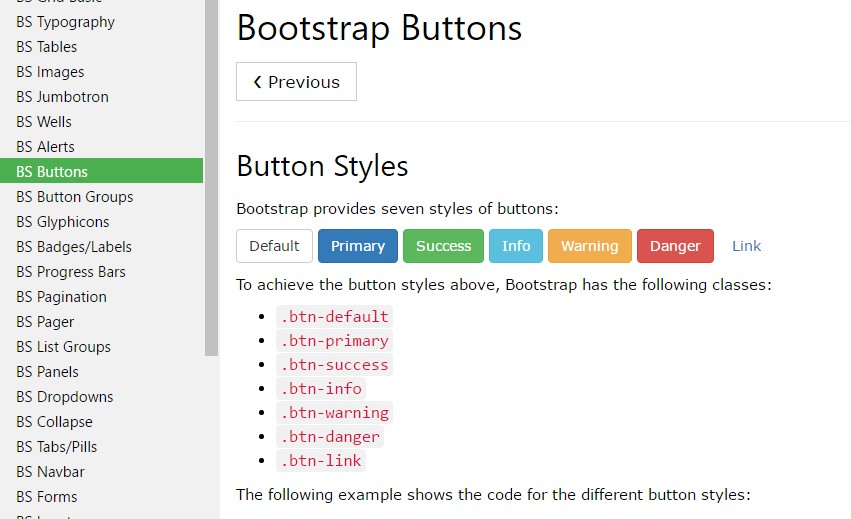
The semantic classes are the same in number as in the last version yet with several enhancements-- the hardly used default Bootstrap Button usually coming with no meaning has been dropped in order to get substituted by the more subtle and intuitive secondary button styling so right now the semantic classes are:
Primary
.btn-primarySecondary
.btn-secondary.btn-default.btn-infoSuccess
.btn-successWarning
.btn-warningDanger
.btn-dangerAnd Link
.btn-linkJust ensure you first provide the main
.btn<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary">Primary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary">Secondary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-success">Success</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-info">Info</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-warning">Warning</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger">Danger</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-link">Link</button>Tags of the buttons
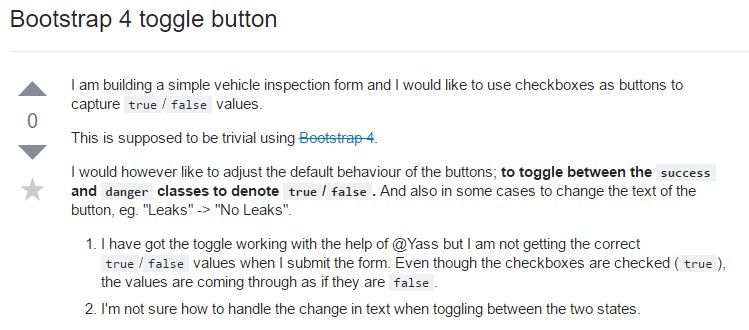
The
.btn<button><a><input><a>role="button"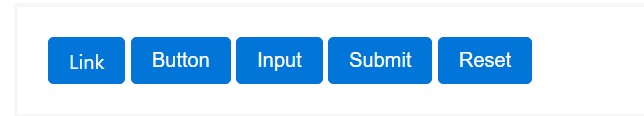
<a class="btn btn-primary" href="#" role="button">Link</a>
<button class="btn btn-primary" type="submit">Button</button>
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="button" value="Input">
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="submit" value="Submit">
<input class="btn btn-primary" type="reset" value="Reset">These are however the fifty percent of the achievable looks you are able to enhance your buttons in Bootstrap 4 ever since the new version of the framework at the same time brings us a brand-new suggestive and beautiful way to design our buttons keeping the semantic we right now have-- the outline procedure ( additional info).
The outline process
The pure background with no border gets removed and replaced by an outline with some text with the affiliated coloring. Refining the classes is truly simple-- just add
outlineOutlined Main button comes to be
.btn-outline-primaryOutlined Second -
.btn-outline-secondaryCrucial factor to note here is there really is no such thing as outlined link button so the outlined buttons are actually six, not seven .
Reinstate the default modifier classes with the
.btn-outline-*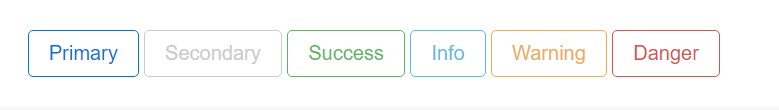
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-primary">Primary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-secondary">Secondary</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-success">Success</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-info">Info</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-warning">Warning</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-outline-danger">Danger</button>Special text
Nevertheless the semantic button classes and outlined appearances are really excellent it is important to bear in mind some of the page's guests won't really have the capacity to check out them in this way whenever you do have some a bit more special message you would love to add in to your buttons-- make sure alongside the graphical means you also include a few words describing this to the screen readers hiding them from the page with the
. sr-onlyButtons proportions
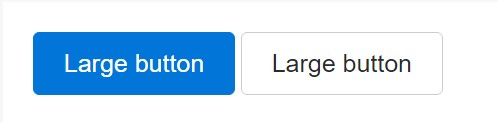
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg">Large button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg">Large button</button>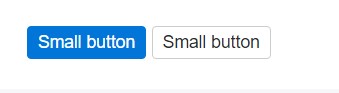
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-sm">Small button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-sm">Small button</button>Create block level buttons-- those that span the full width of a parent-- by adding
.btn-block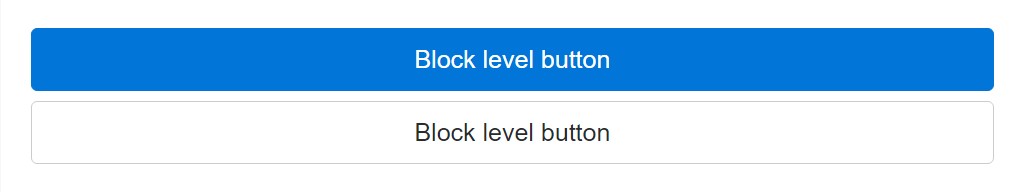
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg btn-block">Block level button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg btn-block">Block level button</button>Active setting
Buttons will appear pressed (with a darker background, darker border, and inset shadow) when active.
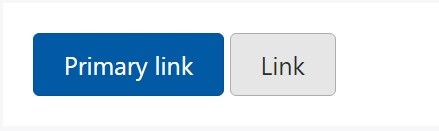
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg active" role="button" aria-pressed="true">Primary link</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg active" role="button" aria-pressed="true">Link</a>Disabled mechanism
Force buttons appear out of service through bring in the
disabled<button>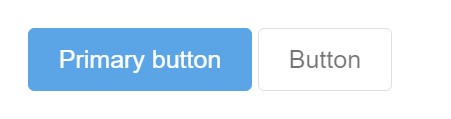
<button type="button" class="btn btn-lg btn-primary" disabled>Primary button</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg" disabled>Button</button>Disabled buttons operating the
<a>-
<a>.disabled- Several future-friendly styles are included to disable all pointer-events on anchor buttons. In browsers that assist that property, you will not see the disabled arrow whatsoever.
- Disabled buttons really should incorporate the
aria-disabled="true"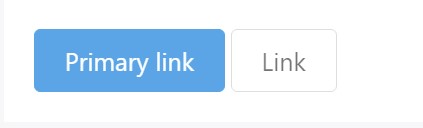
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary btn-lg disabled" role="button" aria-disabled="true">Primary link</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-secondary btn-lg disabled" role="button" aria-disabled="true">Link</a>Link functions caveat
In addition, even in browsers that do support pointer-events: none, keyboard navigation remains unaffected, meaning that sighted keyboard users and users of assistive technologies will still be able to activate these links.
Toggle function
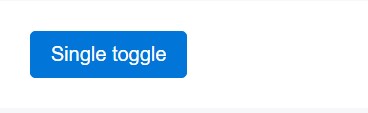
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" data-toggle="button" aria-pressed="false" autocomplete="off">
Single toggle
</button>A bit more buttons: checkbox and also radio
The checked state for these buttons is only updated via click event on the button.
Take note that pre-checked buttons need you to manually put in the
.active<label>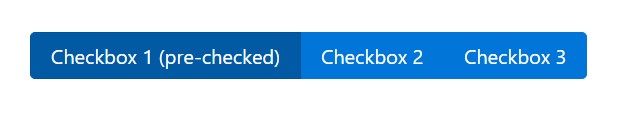
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons">
<label class="btn btn-primary active">
<input type="checkbox" checked autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 1 (pre-checked)
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 2
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="checkbox" autocomplete="off"> Checkbox 3
</label>
</div>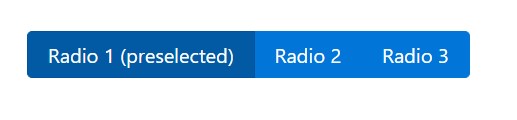
<div class="btn-group" data-toggle="buttons">
<label class="btn btn-primary active">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option1" autocomplete="off" checked> Radio 1 (preselected)
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option2" autocomplete="off"> Radio 2
</label>
<label class="btn btn-primary">
<input type="radio" name="options" id="option3" autocomplete="off"> Radio 3
</label>
</div>Methods
$().button('toggle')Final thoughts
Generally in the new version of the most popular mobile first framework the buttons evolved aiming to become more legible, more easy and friendly to use on smaller screen and much more powerful in expressive means with the brand new outlined appearance. Now all they need is to be placed in your next great page.
Check out a number of online video guide relating to Bootstrap buttons
Related topics:
Bootstrap buttons approved documentation
W3schools:Bootstrap buttons tutorial
Bootstrap Toggle button